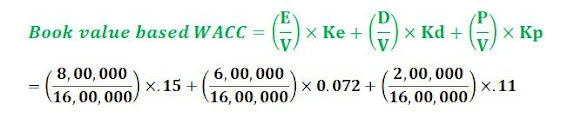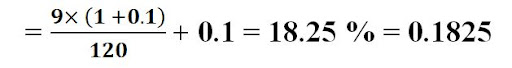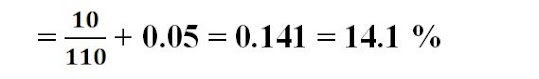Links to Financial Management notes: -
Time Value of Money
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-formulae-financial.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-i-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-2-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-3-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/time-value-of-money-i-financial.html
Leverage Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/financial-management-notes-leverage.html
Cost of Capital
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/cost-of-capital-solved-problems.html
EBIT – EPS Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/ebit-eps-analysis-financial-break-even.html
Capital Structure Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/02/capital-structure-theories-solved.html
Planning & Designing of Capital Structure
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/03/planning-designing-of-capital-structure.html
Estimation of Cash Flow in Capital Budgeting
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-1-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-2-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-3-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/03/estimation-of-cash-flow-in-capital.html
Techniques of Capital Budgeting
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/techniques-of-capital-budgeting.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/capital-budgeting-i-httprblacademycom.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/financial-management-capital-budgeting.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved_2.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved_14.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved.html
Net Proceed (NP) = Face Value or Par Value –
Floatation Cost + Premium on issue – Discount on
issue
Net Proceed = Market Value – Floatation Cost +
Premium on issue – Discount on issue
PD = Preference Dividend
RV = Redeemable Value
Cost of Equity Share (Ke) =
# 1. Zero Growth Dividend
Ke = D1 / P0
# 2. Constant Growth rate in Dividend perpetually
Ke = (D1 /P0) + g
P0 = D1 / (Ke – g)
D1 = D0 (1+ g)
D1 = Expected Dividend
D0 = Current Dividend
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
CAPM Model
Ke = Rf + (Rm - Rf)
× ß
Rf = Risk free rate
Rm = market return
ß = Beta
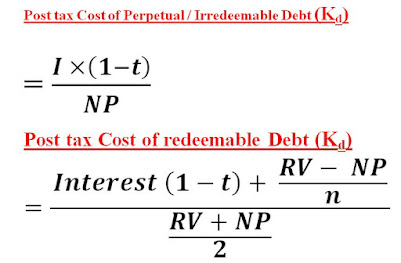
Cost of Loan (KL) = I (1- t )
Book Based WACC (K0) = (E/V) × Ke + (D/V)
× Kd + (P.S./V) × KP + (L/V) × KL +(R&S/V)
× Ke + (R.E./V) × Ke
Market Based WACC (K0) = (E/V) × Ke +
(D/V) × Kd + (P.S./V) × KP + (L/V) × KL
Book Value of Firm = E + D + P.S + L + R.E. + R&S
Market Value of Firm = E + D + P.S + L
E= Value of Equity
D = Value of Debt
P.S. = Value of Preference Share
L = Value of Loan
R.E. = Value of Retained Earnings
R & S = Value of Reserve & Surplus
V= Value of Firm
While calculating WACC based on Market value,
Reserve & Surplus and Retained earnings are not considered as it is
absorbed in market value of equity share. Alternatively we can divide market
value of Equity shares in the ratio of book value of Equity Share and Reserve
& Surplus / Retained Earnings and then include Market value of Reserve
& Surplus / Retained earnings while calculating WACC based on Market value.(Refer
question 16)
Cost of Capital Solved Problems
1. ABC Ltd. issues 13 % debentures of face
value of Rs. 100 each, redeemable at the end of 10 years. The debentures are
issued at par and the flotation cost is estimated to be 5 %. Find out the cost
of capital of debentures given that the firm has 40% tax rate.
Solution
RV = Redeemable Value
NP = Net proceed = Face Value – Floatation Cost
= Rs 100 – Rs. 5 = Rs. 95
I = Interest amount = 13% of Rs.100 = Rs.13
n = Maturity Period of Debenture or Bond
2. ABC Ltd. issues 12% Preference shares
of face value of Rs. 100 each at a flotation cost of 4%. Find out the cost of
capital of preference share if (i) the preference shares are irredeemable, and
(i) if the preference shares are redeemable after 10 years at a premium of 10%.
Solution
PD = Preference Dividend = 12% of Rs. 100 = Rs.12
RV = Redeemable Value = FV + Premium on redemption = Rs.100 +
Rs. 10 = Rs. 110
NP = Face Value / Par Value + Premium on issue – Floatation Cost
= 100 + 0 – 4 = Rs. 96
n= Maturity Period =10 years
3. ABC Ltd. has just declared and paid a
dividend at the rate of 20 % on the equity share of Rs. 100 each. The expected
future growth rate in dividends is 15%. Find out the cost of capital of equity
shares given that the present market value of the share is Rs. 170.
Solution
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
= + 0.15 = 28.53 % = 0.2853
D1 = D0 × (1 + g) = Expected Dividend
D0 = Current Dividend = 20 % of Rs.100 = Rs. 20
g = Growth rate = 15% = .15
P0 = Current Market Price = Rs.170
4. The share of ABC Ltd. is presently traded
at Rs. 60 and the company is expected to pay dividends of Rs. 4 per share with
a growth rate expected at 10% per annum. It plans to raise fresh equity share
capital. The merchant banker has suggested that an underpricing of Rs. 2 is
necessary in pricing the new issue besides involving a cost of Re 1 per share
on miscellaneous expenses. Find out the cost of existing equity shares as well
as the new equity given that the dividend rate and growth rate are not expected
to change.
Solution
Cost of existing Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
Cost of new Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
Net Proceed (NP) = MP (P0) – Underpricing – Miscellaneous expenses = Rs. 60 – Rs. 2 – Re 1 = Rs.575.Assuming that the firm pays tax at a 30% rate, compute the after tax cost of capital in the following cases:
(a) A 13.5% preference shares sold at par.
(b) A perpetual bond sold at par, coupon
rate being 12.5%.
(c) A ten year 9 % Rs. 1,000 per bond sold
at 950.
(d) A common share selling at a market
price of Rs. 120 and paying a current dividend of Rs. 10 per share which is expected
to grow at a rate of 10 %.
(e) 15 %.Preference Shares of Rs. 100
each, issued at 10 % premium, redeemable at par after 6 years. Flotation cost
is Rs. 12 and Dividend Distribution Tax is 20 %. Use both methods.
(f) 12% Debentures of face value of Rs. 1000
each redeemable at par after 5 years, flotation cost being 5%. Use both methods
given the tax rate @30%.
Solution
(a) A 13.5% preference shares sold at par.
After tax Cost of Preference Share (Kp) =
13.5 % = 0.135
(b) A perpetual bond sold at par, coupon
rate being 12.5%.
After tax Cost of Perpetual Bond (Kd) =
Interest rate × (1 – tax rate)
= 12.5 % × (1-0.3) = 0.0875 = 8.75 %
(c) A ten year 9 % Rs. 1,000 per bond sold
at 950.
After tax Cost of redeemable Debenture =
= (63 + 5) / 975 = 6.97 % = 0.0697
RV = Redeemable Value
NP = Net proceed
I = Interest amount
n = Maturity Period of Debenture / Bond
(d) A common share selling at a market
price of Rs. 120 and paying a current dividend of Rs. 10 per share which is
expected to grow at a rate of 10 %.
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
=
D1 = D0 × (1 + g) = Expected Dividend
D0 = Current Dividend
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
(e) 15 %.Preference Shares of Rs. 100
each, issued at 10 % premium, redeemable at par after 6 years. Flotation cost
is Rs. 12 and Dividend Distribution Tax is 20 %. Use both methods.
After tax Cost of Preference Share Kp =
PD = Preference Dividend = 15
DDT = Dividend Distribution Tax = 20 % of PD = Rs. 3
RV = Redeemable Value = Rs.100
NP = Face Value / Par Value + Premium on issue – Floatation Cost
= 100 + 10 – 12 = Rs. 98
n= Maturity Period = 6 years
Second Method: Using Interpolation Method:
NP = PD including DDT × PVAF Kp, 6 + RV × PVFKp,
6
Considering KP at 18 %
= 18 × 3.498 + 100 × 0.37 = Rs. 99.964
Considering KP at 19 %
= 18 × 3.410 + 100 × 0.352 = Rs. 96.58
Now using Interpolation Formula-
(f) 13% Debentures of face value of Rs. 1000 each redeemable at par after 5 years, flotation cost being 5%. Use both methods given the tax rate @30%.
After tax Cost of redeemable Debenture =
= 10.36 % = 0.1036
Second Method: Using Interpolation Method:
NP = Interest amount after tax × PVAF Kd, 5 + RV ×
PVF Kd, 5
Considering KP at 10 %
= 130 × (1- 0.3) × 3.791 + 1,000 × 0.621 = Rs. 965.98
Considering KP at 11 %
= 130 (1-0.3) × 3.696 + 1,000 × 0.593 = Rs. 929.34
Now using Interpolation Formula-
6. RBL Company has the following capital
structure on 1 July, 2021
|
|
Number/ Units |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Equity Shares |
40,000 |
8,00,000 |
|
11% Preference Shares |
|
2,00,000 |
|
12 % Debentures |
|
6,00,000 |
|
Total |
|
16,00,000 |
The share of a company currently sells for
Rs. 25. It is expected that the company will pay a dividend of Rs. 2 per share
which will grow at 7 % forever. Assume a 40 per cent tax rate; you are required
to compute weighted average cost of capital on existing capital structure.
Solution
D1
= Expected Dividend
P0
= Market Price of Equity Share
g
= Growth rate
I
= Interest rate on Debenture
E
= Value of Equity Share
D
= Value of Debenture
P
= Value of Preference Share
V
= Value of Firm = E + D + P
Cost of Equity (Ke) =
(D1 / P0) + g = 2/25 + .07 = 0.15 = 15 %
Post Tax Cost of Debt (Kd) = I × (1 - t) = 0.12 × (1-0.4) =
0.072 = 7.2%
Cost of Preference Share (Kp) = 0.11 = 11 %
=
0.075 + 0.027 + 0.01375 = 0.1158 = 11.58%
7. RBL company's share is quoted in the
market at Rs. 20 currently. The company has paid dividend of Rs. 2 per share
and the investor's market expects a growth rate of 10 percent per year. You are
required to compute-
(I) The Company’s Equity Cost of Capital.
(II) If the company's cost of capital is 15
per cent and the anticipated growth rate is 10 per cent per annum, calculate
market price if the dividend of Rs. 2 is to be paid at the end of one year.
Solution
I.
Cost of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
=
D1 = D0 × (1 + g) = Expected Dividend
D0 = Current Dividend = Rs. 2
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
II. Market Price of Share
D1 = Rs. 2 = Expected Dividend
8. Equity shares (Face value of Rs.10 each) of RBL Ltd. are
being quoted at PE of 8 times. The retained earnings of the company are Rs. 6
at 40 %.
(I) find out the cost of equity, if the
growth rate of the firm is 10%.
(II) Find out the indicated market price
of the shares, given that
Ke remains as above and growth
rate increases to 13%.
(III) If Ke of the firm is 16%
and growth rate being 10%, then what is the indicated market price of the
equity share?
Solution
I. Retention ratio = 0.4 = 40 % of EPS = Rs. 6
=> 0.4 EPS = Rs. 6
So, EPS = Rs. 6/0.4 = Rs. 15
Retained Earnings per Share = Rs. 6
EPS = Earnings per Share = E0
MPS = Market Price per Share = P0
PE ratio = MPS / EPS = P0 / E0
MPS = EPS × PE Ratio = Rs. 15 × 8 = Rs. 120
Dividend Payout Ratio =
1 – retention ratio = 1- 0.4 = 0.6 = 60 %
Dividend Per Share (D0)
= 60 % of EPS = 0.6 × Rs. 15 = Rs. 9
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
= 18.25 % = 0.1825
D1 = D0 × (1 + g) = Expected Dividend
D0 = Current Dividend = Rs. 9
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
II. Market
Price of Share (Po)
9. Shares of XYZ Ltd. are currently
selling at Rs. 170 each. The company has been regularly paying dividends for
last several years as follows:
|
Years |
Amount |
|
1 |
12.00 |
|
2 |
12.72 |
|
3 |
13.48 |
|
4 |
14.29 |
|
5 |
15.15 |
|
6 |
16.07 |
Find out the growth rate of the company,
given that the company follows a policy of fixed DP Ratio. Also find out the
cost of equity of the company.
Solution
Cumulative Growth rate for 5 years = 16.07 /12.00 =
1.339
In FVF table, the value nearest to 1.339 for 5 years
is 1.338 at 6 % rate. So annual growth rate = 6 %
Second way to calculate growth rate in this case is
calculating percentage increase in amount year on year since company follows a
policy of fixed DP Ratio; hence growth rate will be same Year over Year
|
Years |
Amount |
%age
Change |
|
1 |
12.00 |
------- |
|
2 |
12.72 |
(12.72
– 12) /12 = 0.06 or 6 % |
|
3 |
13.48 |
(13.48
- 12.72 ) /12.72 = 0.06 or 6 % |
|
4 |
14.29 |
(14.29
– 13.48) /13.48 = 0.06 or 6 % |
|
5 |
15.15 |
(15.15
– 14.29) /14.29 = 0.06 or 6 % |
|
6 |
16.07 |
(16.07
– 15.15) /15.15 = 0.06 or 6 % |
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
D0 = Dividend paid in 6th year
(since 6th year is current year in which share is trading at Rs.
170)
10. The following figures are taken from
the current balance sheet of Diwakar & Co.
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital of Rs. 10 each |
8,00,000 |
|
Share / Security Premium |
2,00,000 |
|
Reserves |
6,00,000 |
|
Shareholders’ Funds |
16,00,000 |
|
14 % Perpetual Debentures of Rs. 100 each |
4,00,000 |
An annual ordinary dividend of Rs. 3 per
share has just been paid. In the past, ordinary dividends have grown at a rate
of 10 per cent per annum and this rate of growth is expected to continue.
Annual interest has recently been paid on the debentures. The ordinary shares
are currently quoted at Rs. 30 and the debentures at 80 per cent Ignore
taxation. You are required to estimate the weighted average cost of capital
(based on market values) for Diwakar & Co.
Solution
D0
= Current Dividend paid = Rs. 3
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
=
Cost of Perpetual Debentures = Interest / NP or MP
= 14/80 = 0.175 = 17.5%
NP = Net Proceed
MP = Market Price of Debenture
Market Value of Equity Share (E) = Market Price per
Share × no. of Equity Shares = Rs. 30 × Rs. 8,00,000 / 10 = Rs. 24,00,000.
Market Value of Perpetual Debenture (D) = Market
Price per Debenture × no. of Debentures = Rs. 80 × Rs. 4,00,000 / 100 = Rs.
3,20,000.
Market Value of Firm (V) = Market Value of Equity
Share + Market Value of Perpetual Debenture = Rs. 24,00,000 + Rs. 3,20,000 =
Rs. 27,20,000
WACC (based on market values) = (E/V) × Ke +
(D/V) × Kd
= (24,00,000 / 27,20,000) × 0.21 + (3,20,000 /
27,20,000) × 0.175 = 0.185 + 0.021 = 0.206 = 20.6 %
11. The following information has been
extracted from the balance sheet of RBL Ltd.
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital |
5,00,00,000 |
|
12% Debentures |
5,00,00,000 |
|
18% Term loan |
12,00,00,000 |
|
Total |
22,00,00,000 |
(a) Determine the weighted average cost of
capital of the company. It had been paying dividends at a consistent rate of
20% per annum. Shares and Debentures are being traded at par. Tax rate is 40%.
(b) What difference will it make if the
current price of share (Face Value Rs.100) is Rs. 170?
Solution
a. Cost of Debenture (Kd) = I (1- t)
= 12% × (1-0.4) = 7.2% = 0.072
Cost of Term Loan (KL) = I (1-t)
=18% × (1-0.4) = 10.8% = 0.108
Cost of equity (Ke) = Dividend / NP or P0
= 20 / 100 = 0.2
(Assuming Par value of Equity share to be Rs. 100;
Dividend = 20 % of Face value = 20 % of Rs. 100)
Note: Since Market Price of Share and growth rate is
not given and there is no premium or discount on issue of share and also no
floatation cost is mentioned in the question, hence face value / Par value has
been considered as Net proceed or Market Price of equity Share.
WACC = (E/V) × Ke + (D/V) × Kd
+ (TL / V) × KL
= (5,00,00,000 / 22,00,00,000) × 0.2 + (5,00,00,000
/ 22,00,00,000) × 0.072 + (12,00,00,000 / 22,00,00,000) × 0.108
=0.045 + 0.0163 +0.0589 = 0.1202 = 12.02%
b. Cost of equity (Ke) = Dividend / P0
= 20 / 170 = 0.1176
Cost of Term Loan (KL) and Cost of
Debenture (Kd) will remain same.
WACC (based on Book Value of company) = (E/V) × Ke
+ (D/V) × Kd + (TL / V) × KL
= (5,00,00,000 / 22,00,00,000) × 0.1176 +
(5,00,00,000 / 22,00,00,000) × 0.072 + (12,00,00,000 / 22,00,00,000) × 0.108
=0.027 + 0.0163 +0.0589 = 0.102 = 10.2%
12. The following information is available
from the Balance Sheet of a Company:
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 20,000 shares of Rs. 10 each |
2,00,000 |
|
Reserve & Surplus |
1,40,000 |
|
8 % Debentures |
1,60,000 |
The rate of tax for the company is 50%.
Current level of Equity Dividend is 15%. Calculate the weighted average cost of
capital using the above figures.
Solution
|
|
Book
Value |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Equity
Share Capital |
2,00,000 |
2,00,000/5,00,000
= 0.4 |
.15 |
0.06 |
|
Reserve
& Surplus |
1,40,000 |
1,40,000/5,00,000
= 0.28 |
.15 |
0.042 |
|
8
% Debentures |
1,60,000 |
1,60,000/5,00,000
= 0.32 |
0.08
× (1-0.5) =0.04 |
0.0128 |
|
Total
Value of Firm |
4,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost= 0.06 + 0.042 + 0.0128 = 0.1148 |
||
13. In considering the most desirable
capital structure for a company, the following estimates of the cost of debt
capital (after tax) have been made at various levels of debt-equity mix:
|
Debt as percentage of Total Capital Employed |
Cost of Debt (Kd) % |
Cost of Equity (Ke )% |
|
0 |
7.0 |
20.0 |
|
10 |
7.0 |
20.0 |
|
20 |
7.0 |
20.5 |
|
30 |
7.5 |
21.0 |
|
40 |
8.0 |
22.0 |
|
50 |
8.5 |
25.0 |
|
60 |
9.5 |
27.0 |
You are required to find out the weighted
average cost of capital of the firm for different proportions of debt and
optimal capital structure.
Solution
|
Debt % |
Kd |
Equity % |
Ke |
WACC
= (Debt % × Kd) +( Equity %× Ke) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
7.0 |
100 |
20.0 |
20% |
|
10 |
7.0 |
90 |
20.0 |
18.7% |
|
20 |
7.0 |
80 |
20.5 |
17.8% |
|
30 |
7.5 |
70 |
21.0 |
16.95% |
|
40 |
8.0 |
60 |
22.0 |
16.4% |
|
50 |
8.5 |
50 |
25.0 |
16.75% |
|
60 |
9.5 |
40 |
27.0 |
16.5% |
Since WACC is lowest with 40 % debt and 60 % equity.
Hence, optimal capital Structure will be capital mix of 40:60 Debt- equity
ratio.
Since value of debt and equity is given in
percentage, there is no need to calculate weight of Debt and equity for WACC
calculation as it will remain same. Since value of firm will be 100 % and if we
divide debt % with firm value percentage or equity % with firm value
percentage, result will remain same.
14. A company with net operating income of
Rs. 3, 00,000 is attempting to evaluate a number of possible capital
structures, given below. Which of the capital structure will you recommend and
why?
|
Capital Structure |
Debt in Capital Structure (Rs.) |
Kd (Cost of Debt) |
Ke (Cost of Equity) |
|
1 |
1,00,000 |
10.0 |
12.0 |
|
2 |
2,00,000 |
10.0 |
12.0 |
|
3 |
3,00,000 |
10.0 |
12.0 |
|
4 |
4,00,000 |
10.0 |
12.5 |
|
5 |
5,00,000 |
11.0 |
13.5 |
|
6 |
6,00,000 |
12.0 |
15.0 |
|
7 |
7,00,000 |
14.0 |
18.0 |
Solution
|
Capital Structure |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
EBIT |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
|
Less:
Interest |
(10,000) |
(20,000) |
(30,000) |
(40,000) |
(55,000) |
(72,000) |
(98,000) |
|
EBT
/ PAT |
2,90,000 |
2,80,000 |
2,70,000 |
2,60,000 |
2,45,000 |
2,28,000 |
2,02,000 |
|
Ke |
12.0 |
12.0 |
12.0 |
12.5 |
13.5 |
15.0 |
18.0 |
|
Value of Equity |
24,16,667 |
23,33,333 |
22,50,000 |
20,80,000 |
18,14,815 |
15,20,000 |
11,22,222 |
|
Value
of Debt |
1,00,000 |
2,00,000 |
3,00,000 |
4,00,000 |
5,00,000 |
6,00,000 |
7,00,000 |
|
Value of Firm |
25,16,667 |
25,33,333 |
25,50,000 |
24,80,000 |
23,14,815 |
21,20,000 |
18,22,220 |
Value of Equity = PAT / Ke
Value of Firm = Value of Debt + Value of Equity
Since, Value of Firm is highest for third Capital structure;
hence third capital structure should be selected by company.
15. POR & Co. has the following
capital structure as on Dec. 31.
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 5,000 shares of Rs. 100 each |
5,00,000 |
|
9 % Preference Shares |
2,00,000 |
|
10 % Debentures |
3,00,000 |
The equity shares of the company are
quoted at Rs. 110 and the company is expected to declare a dividend of Rs. 10
per share for the next year. The company has registered a dividend growth rate
of 5% which is expected to be maintained.
(I)
Assuming the tax rate applicable to the company at 40%, calculate the weighted
average cost of capital, and
(II) Assuming that the company can raise
additional term loan at 12% for Rs. 10,00,000 to finance its expansion,
calculate the revised WACC. The company's expectation is that the business risk
associated with new financing may bring down the market price from Rs. 110 to
Rs. 90 per share.
Solution
I. Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
Post TaxCost of Debenture (Kd) = I × (1-t) = 0.1 × (1-0.4) =0.06 = 6 %
Cost of Preference Share (Kp) = 0.09 = 9%
|
|
Book
Value |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Equity
Share Capital |
5,00,000 |
5,00,000/10,00,000
= 0.5 |
.141 |
0.0705 |
|
9
% Preference Shares |
2,00,000 |
2,00,000/10,00,000
= 0.20 |
.09 |
0.018 |
|
10
% Debentures |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000/10,00,000
= 0.30 |
.06 |
0.018 |
|
Total
Value of Firm |
20,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost= 0.0705 + 0.018 + 0.018 = 0.1065 = 10.65% |
||
II. Cost of Term Loan (Kl) = I × (1- t) =
.12 × .6 = 0.072 = 7.2%
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
|
|
Book
Value |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Equity
Share Capital |
5,00,000 |
5,00,000/20,00,000
= 0.25 |
.1611 |
0.0403 |
|
9
% Preference Shares |
2,00,000 |
2,00,000/20,00,000
= 0.10 |
.09 |
0.018 |
|
10
% Debentures |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000/20,00,000
= 0.15 |
.06 |
0.018 |
|
12
% Term Loan |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/20,00,000
= 0.5 |
0.072 |
0.036 |
|
Total
Value of Firm |
10,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost= 0.0403 + 0.018 + 0.018 + 0.036= 0.1123 = 11.23% |
||
16. International Foods Limited has the
following capital structure:
|
Particulars |
Book Value (Rs.) |
Market Value (Rs) |
|
|
|
|
|
Share Capital- 25,000 shares of Rs. 10 each |
2,50,000 |
4,50,000 |
|
13% Preference Capital (500 shares of Rs. 100 each) |
50,000 |
45,000 |
|
Reserves and Surplus |
1,50,000 |
---------- |
|
12 % Debentures (1500 debentures of 100 each) |
1,50,000 |
1,20,000 |
|
Total |
6,00,000 |
6,15,000 |
The expected dividend per share is Rs.2 and
the dividend per share is expected to grow at a rate of 10 percent forever. Preference
shares are redeemable after 5 years at par whereas debentures are redeemable
after 10 years at 10 % premium. The tax rate for the company is 30 per cent.
You are required to compute the weighted average cost of capital for the
existing capital structure using market value as weights.
Solution
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
0.2111 = 21.11 %
D1 = Expected Dividend
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
P0 = Market Value (MV) of Equity / Total no. of
Equity Shares = Rs. 4,50,000 / 25,000 = Rs. 18
After tax Cost of Preference Share Kp =
PD = Preference Dividend = 13
RV = Redeemable Value = Rs.100
MP = Market Price
n= Maturity Period = 5 years
MP = Market Value of Pref. Share / Total no. of Pref. Shares
= Rs. 45,000 / 500 = Rs. 90
After tax Cost of redeemable Debenture =
RV = Redeemable Value = Par value + Premium on redemption = Rs. 100 + 10 % of Rs. 100 = Rs. 110
I = Interest amount
n = Maturity Period of Debenture / Bond = 10 years
MP = Market Price
MP = Market Value of Debentures / Total no. of Debentures
= Rs. 1,20,000 / 1,500 = Rs. 80
|
|
Market
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
4,50,000 |
4,50,000/6,15,000
= 0.732 |
0.2111 |
0.1545 |
|
13%
Preference Capital |
45,000 |
45,000/6,15,000
= 0.0732 |
.1579 |
0.0116 |
|
Reserves
and Surplus |
________ |
__________ |
___ |
____ |
|
12
% Debentures |
1,20,000 |
1,20,000/6,15,000
= 0.1951 |
0.12 |
0.0234 |
|
Total |
6,15,000 |
WACC based on Market
Value = ∑ Weighted Cost= 0.1545 + 0.0116+ 0.0234
= 0.1895 = 18.95% |
||
Note: While calculating WACC based on Market value,
Reserve & Surplus and Retained earnings are not considered as it is
absorbed in market value of equity share. Alternatively we can divide market
value of Equity shares in the ratio of book value of Equity Share and Reserve
& Surplus and then include Market value of Reserve & Surplus while
calculating WACC based on Market value. In this case,
Cost of Reserve & Surplus (KR&S)
= Cost of Share Capital (Ke)
In this case Market value of Equity that is Rs.
4,50,000 can be divided into Equity Share & Reserve & Surplus in the
ration of book value of Equity Share & Reserve & Surplus That is in the
ratio of 2,50,000 : 1,50,000.
|
|
Market
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
2,81,250 |
2,81,250/6,15,000
= 0.4573 |
0.2111 |
0.0965 |
|
13%
Preference Capital |
45,000 |
45,000/6,15,000
= 0.0732 |
.1579 |
0.0116 |
|
Reserves
and Surplus |
1,68,750 |
1,68,750/6,15,000
= 0.2744 |
0.2111 |
0.058 |
|
12
% Debentures |
1,20,000 |
1,20,000/6,15,000
= 0.1951 |
0.12 |
0.0234 |
|
Total |
6,15,000 |
WACC based on Market
Value = ∑ Weighted Cost= 0.0965 + 0.0116 + 0.058
+ 0.0234 = 0.1895 = 18.95% |
||
17. A Limited has the following capital
structure:
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 2,00,000 shares of Rs. 20 each |
40,00,000 |
|
6 % Preference Shares |
10,00,000 |
|
8 % Debentures |
30,00,000 |
The market price of the company's equity
share is Rs. 30. It is expected that company will pay a dividend of Rs. 2 per
share at the end of current year, which will grow at 10 per cent forever. The
tax rate is 30 per cent. You are required to compute the following:
(a) A weighted average cost of capital
based on existing capital structure.
(b) The new weighted average cost of
capital if the company raises an additional Rs. 20,00,000 debt by issuing 12 %
debentures. This would result in increasing the expected dividend to Rs. 3 and
leave the growth rate unchanged but the price of share will fall to Rs. 20 per
share.
(c) The cost of capital if in (b) above,
growth rate increases to 12 percent.
Solution
a.
Cost of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
D1 = Expected Dividend
g = Growth rate
P0 = Current Market Price
Post Tax Cost of Debenture (Kd) =
Interest rate × (1 - t)
= 0.08 × (1 - 0.3) = 0.056 = 5.6%
Cost of Preference Share (KP) = 6% = 0.06
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
40,00,000 |
40,00,000
/ 80,00,000 =0.5 |
0.1667 |
0.0834 |
|
6%
Preference Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000
/ 80,00,000 = 0.125 |
.06 |
.0075 |
|
8
% Debentures |
30,00,000 |
30,00,000
/ 80,00,000 =0.375 |
0.056 |
.0210 |
|
Total |
80,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost = 0.0834 + 0.0075 +
0.0210 = 0.1119 = 11.19 % |
||
b. Cost of
Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
= 0.12 × (1 - 0.3) = 0.084 = 8.4 %
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
40,00,000 |
40,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000=0.4 |
0.25 |
0.1 |
|
6%
Preference Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000= 0.1 |
.06 |
0.006 |
|
8
% Debentures |
30,00,000 |
30,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000=0.3 |
0.056 |
0.017 |
|
12
% Debentures |
20,00,000 |
20,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000 = 0.2 |
0.084 |
0.017 |
|
Total |
1,00,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost = 0.1 + 0.006 + 0.017
+ 0.017 = 0.14 = 14 % |
||
c. Cost of
Equity (Ke) = (D1 / Po) + g
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
40,00,000 |
40,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000=0.4 |
0.27 |
0.108 |
|
6%
Preference Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000= 0.1 |
.06 |
0.006 |
|
8
% Debentures |
30,00,000 |
30,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000=0.3 |
0.056 |
0.017 |
|
12
% Debentures |
20,00,000 |
20,00,000
/ 1,00,00,000 = 0.2 |
0.084 |
0.017 |
|
Total |
1,00,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost = 0.108 + 0.006 +
0.017 + 0.017 = 0.148 = 14.8 % |
||
18. An electric equipment manufacturing
company wishes to determine the weighted average cost of capital for evaluating
capital budgeting projects. You have been supplied with the following
information:
|
Liabilities |
Amount (Rs.) |
Assets |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Equity share capital |
12,00,000
|
Fixed Assets
|
25,00,000
|
|
Pref. share capital |
4,50,000 |
Current Assets |
15,00,000 |
|
Retained Earnings |
4,50,000 |
|
|
|
Debentures |
9,00,000 |
|
|
|
Current Liabilities |
10,00,000 |
|
|
|
|
40,00,000 |
|
40,00,000 |
Additional Information:
(a) 10 years 10% Debentures of 2,500 face
value, redeemable at 5% premium can be sold at par. 2% Flotation costs.
(b) 12% Preference shares: Sale price Rs.
100 per share, 2% Flotation costs.
(c)
Equity shares: Sale price Rs. 120 per share, Flotation costs- Rs. 5 per
share.
The corporate tax rate is 40% and the
expected growth in equity dividend is 10 % per year. The expected dividend at
the end of the current financial year is Rs.10 per share. Assume that the
company is satisfied with its present capital structure and intends to maintain
it.
Solution
Cost of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / NP) + g
NP = Sales Price – Floatation Cost =
Rs.120 – Rs.5 = Rs.115
After tax Cost of redeemable Debenture =
RV = Face Value + 5 % Premium on redemption
= Rs. 2,500 + Rs.125 = Rs.2,625
NP = Face Value – Floatation cost = Rs.2500 – 2 % of Rs.2500 =
Rs.2,450
Cost of Irredeemable Preference Share (Kp) = PD / NP
= 12/98 = 0.1224 = 12.24%
NP = NP = Face Value – Floatation cost = Rs. 100 – 2 = Rs.98
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
12,00,000 |
12,00,000/30,00,000=
0.4 |
0.187 |
.0748 |
|
Retained
Earnings |
4,50,000 |
4,50,000/30,00,000
=.15 |
0.187 |
.0281 |
|
12%
Preference Capital |
4,50,000 |
4,50,000/30,00,000
=.15 |
0.1224 |
.0183 |
|
10
% Debentures |
9,00,000 |
9,00,000/30,00,000
=0.3 |
0.076 |
.0228 |
|
Total |
30,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted Cost
=.0748+.0281+.0183+.0228= .1212 = 12.12% |
||
19. The latest Balance Sheet of RBL Ltd.
is given below:
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 50,000 shares of Rs. 10 each |
5,00,000 |
|
Security Premium |
1,00,000 |
|
Retained Profit |
6,00,000 |
|
10 % Preference Shares – 16,000 shares |
4,00,000 |
|
15 % Perpetual Debt – 6000 debentures |
6,00,000 |
The ordinary shares are currently priced
at Rs. 40 ex-dividend each and Rs.25 preference share is priced at Rs. 25
cum-dividend. The debentures are selling at 110 per cent ex-interest and tax is
paid by RBL Ltd. at 40 per cent. RBL Ltd's cost of equity has been estimated at
20 per cent. Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (based on market
value) WACC of D Ltd.
Solution
Ke = .20
Cost of Perpetual debt (Kd) =
=0.082
Cost of Irredeemable Preference Share (Kp) = PD / NP
= 2.5 / (25 – 2.5) = 0.1111
Note: Since Price of Preference share is including
dividend that is cum dividend as given in the question, hence dividend has been
subtracted from Market Price.
|
|
Market
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
40×50,000
= 20,00,000 |
0.6623 |
0.2 |
.1325 |
|
10%
Preference Capital |
22.5
× 16,000 =3,60,000 |
.1192 |
0.1111 |
.0132 |
|
15
% Debentures |
110×6,000=6,60,000 |
.2185 |
0.082 |
.018 |
|
Total |
30,20,000 |
WACC based on Market
Value = ∑
Weighted Cost =.1325+.0132+ .018 = .1637 =16.37% |
||
20. Determine the weighted average cost of
capital using (a) book value weights; and (b) market value weights based on the
following information:
|
Book value structure |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 1,00,000 shares of Rs. 10 each |
10,00,000 |
|
Preference shares (2,000 Pref. Shares of Rs.100 each) |
2,00,000 |
|
Debentures ( 8,000 units of Rs.100 each) |
8,00,000 |
|
Total |
20,00,000 |
Recent market prices of all these
securities are: Debentures: Rs. 110 per Debenture; Preference shares: Rs. 120
per share and Equity shares: Rs. 22 per share. External financing opportunities
are:
(i) Rs. 100 per Debenture redeemable at
par, 10 year maturity, 13% coupon rate, 4% flotation cost and sale price Rs. 100;
(ii) Rs. 100 per Preference Share
redeemable at par, 10 year maturity, 14% dividend rate, 5% flotation cost and
sale price 100; and
(iii) Equity shares: Rs. 2 per share
flotation costs and sale price Rs. 22.
Dividend expected on equity shares at the
end of the year is Rs. 2 per share; anticipated growth rate in dividends is 7%.
Company pays all its earnings in the form of dividends. Corporate tax rate is
30%.
Solution
a.
Cost of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / NP) + g
NP = Sales Price – Floatation Cost =
Rs.22 – Rs.2 = Rs.20
After tax Cost of redeemable Debenture =
NP = Face Value – Floatation cost = Rs.100 – 4 % of Rs.100 = Rs.
96
After tax Cost of Preference Share Kp =
NP = Sales Price – Floatation Cost =
Rs.100 – Rs.5 = Rs.95
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/
20,00,000 = 0.5 |
.17 |
0.085 |
|
14%
Preference Capital |
2,00,000 |
2,00,000/
20,00,000 =.1 |
.149 |
0.0149 |
|
13
% Debentures |
8,00,000 |
8,00,000/
20,00,000 =.4 |
.097 |
0.0388 |
|
Total |
20,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted
Cost =.085+.0149+.0388 =.1387 = 13.87% |
||
b.
|
|
Market
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
22
× 1,00,000 =22,00,000 |
.6627 |
.17 |
.1127 |
|
10%
Preference Capital |
120
× 2,000 = 2,40,000 |
.0723 |
.149 |
.0108 |
|
15
% Debentures |
110
× 8,000 = 8,80,000 |
.2650 |
.097 |
.0258 |
|
Total |
33,20,000 |
WACC based on Market
Value = ∑
Weighted Cost =.1127+.0108+ .0258= .1493 =14.93% |
||
21. The following information is provided
in respect of the specific cost of capital of different sources along with the
book value (BV) and market value (MV) weights.
|
Source |
Cost of Capital (%) |
Book Value |
Market Value |
|
Equity share capital |
20 |
.5 |
.55 |
|
Preference shares |
15 |
.2 |
.20 |
|
Debenture |
10 |
.3 |
.25 |
(a) Calculate the Weighted Average Cost of
Capital, WACC, using both the BV and the MV weights.
(b) Calculate the WMCC using marginal weights given that the
company intends to raise additional funds using 50 % long term debts, 30%
preference share and 20% by retaining profits.
Solution
|
Source |
Cost
of Capital (COC) |
Book
Value (BV) |
Market
Value (MV) |
BV
× COC |
MV
×COC |
|
Equity
share capital |
.20 |
.5 |
.55 |
.1 |
.11 |
|
Preference
shares |
.15 |
.2 |
.20 |
.03 |
.03 |
|
Debenture |
.10 |
.3 |
.25 |
.03 |
.025 |
|
|
|
|
|
WACC
based on BV =.16 = 16% |
WACC
based on MV=.175 = 16.5% |
|
Source |
Cost
of Capital (COC) |
Weight |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × COC |
|
Retained
Earnings |
.20 |
.2 |
.04 |
|
Preference
shares |
.15 |
.3 |
.045 |
|
Debenture |
.10 |
.5 |
.05 |
|
|
WMCC = ∑ Weighted Cost = .135=13.5% |
||
22. X Ltd. has assets of Rs. 32,00,000
that have been financed by Rs. 18,00,000 of equity shares (of Rs. 100 each),
General Reserve of Rs. 4,00,000 and Debt of Rs. 10,00,000. For the year ended
31-3-2021, the company's total profits before interest and taxes were Rs. 6, 50,000.
X Ltd. pays 10 % interest on borrowed capital and is in a 30% tax bracket. The
market value of equity as on 31-3-2021 was Rs.150 per share. What was the
weighted average cost of capital? Use market values as weights.
Solution
Cost of debt (Kd) = Interest rate × (1 –
t) = .1 ×.7 = .07 = 7 %
Cost of Equity (Ke) = PAT / MV of Equity
= 3,85,000 / 27,00,000 = 0.1426 = 14.26 %
PAT = (EBIT – Interest) × (1 – t) = (6,50,000 –
1,00,000) ×.7
= 3,85,000
MV of Equity Share = MP of Share × no. of Equity
Shares
= Rs.27,00,000
|
|
Market
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Equity
Share Capital |
27,00,000 |
27,00,000/37,00,000
= .73 |
.1426 |
.1041 |
|
Debt |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/37,00,000
= .27 |
.07 |
.0189 |
|
Total |
37,00,000 |
WACC based on Market
Value = ∑
Weighted Cost = .123 = 12.3% |
||
23. The following is the capital structure of Simons Company Ltd-
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 10,000 shares of Rs. 100 each |
10,00,000 |
|
12 % Preference Shares of Rs. 100 each |
4,00,000 |
|
10 % Debentures |
6,00,000 |
The market price of the company's share is
Rs. 120 and it is expected that a dividend of Rs. 10 per share would be
declared after 1 year. The dividend growth rate is 10%:
(i) If the company is in the 40% Tax
bracket, compute weighted average cost of capital.
(ii) Assuming that in order to finance an
expansion plan, the Company intends to borrow a fund of Rs.10 lacs bearing 12%
rate of interest, what will be the company’s revised weighted average cost of
capital? This financing is expected to increase dividend from Rs. 10 to Rs. 12
per share. However, the market price of equity share is expected to decline
from Rs. 120 to Rs. 110 per share.
Solution
i. Cost of
Equity (Ke) = (D1 / MP) + g
Cost of Debt (Kd) = I × (1 - t) = .1 × (1
– 0.4) = 0.06 = 6%
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/
20,00,000 = 0.5 |
.1833 |
0.092 |
|
12%
Preference Capital |
4,00,000 |
4,00,000/
20,00,000 =.2 |
.12 |
0.024 |
|
10
% Debentures |
6,00,000 |
6,00,000/
20,00,000 =.3 |
.06 |
0.018 |
|
Total |
20,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted
Cost = 0.092 + 0.024 + 0.018 = 0.116 = 11.6 % |
||
ii. Cost of
Equity (Ke) = (D1 / MP) + g
Cost of Pref. Share (Kp) = 0.12
Cost of Debt (Kd) = I × (1 - t) = .1 × (1
– 0.4) = 0.06 = 6%
Cost of Loan / Borrowed Fund (KL) = I ×
(1 - t) = .12 × (1 – 0.4) = 0.072 = 7.2%
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/
30,00,000 = 0.333 |
.2091 |
0.07 |
|
12%
Preference Capital |
4,00,000 |
4,00,000/
30,00,000 =.1333 |
.12 |
0.016 |
|
10
% Debentures |
6,00,000 |
6,00,000/
30,00,000 =.2 |
.06 |
.012 |
|
12
% Borrowed Funds |
10,00,000 |
10,00,000/
30,00,000 = 0.333 |
.072 |
.024 |
|
Total |
30,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted
Cost = 0.07+0.016+.012 + .024 = .122 = 12.2% |
||
24. XYZ Ltd wishes to raise additional
funds of Rs.10,00,000 to take up an investment proposal. Following information
is provided:
|
|
|
|
Retained Earnings |
2,50,000 |
|
Earnings Per share |
5 |
|
Dividend Payout Ratio |
60% |
|
Expected Growth Rate |
10% |
|
Current Market Price of Share
|
30 |
|
Debt- Equity Mix |
30%:70% |
|
Cost of Debts (before tax): Funds up to Rs. 2,00,000 Funds More than 2,00,000 |
10% 12% |
|
Tax Rate |
40% |
You are required to:
(i) Determine the pattern for raising
additional funds.
(ii) Determine the Cost of Equity and Cost
of Retained Earnings.
(iii) Determine the Required Rate of
Return for the new Project.
Solution
i. Debt to be raised – 30 % = Rs. 3,00,000
Equity – 70% = Rs. 7,00,000
Retained Earnings (2,50,000)
Equity fund to be raised = Proportion of Equity
amount – Retained Earnings
= Rs. 7,00,000 – Rs. 2,50,000 = Rs. 4,50,000
After tax Cost of Debt (Kd) = I × (1- t)
= .12 × (1- 0.4) = .072 = 7.2%
ii.
Cost of Equity (Ke) = Cost of Retained Earnings (KRE)
=
(D1 / MP) + g
Current Dividend (D0) = Rs. 3
Expected Dividend (D1) = D0 (1
+ g) = Rs. 3 × 1.1 = Rs.3.3
Dividend Payout Ratio = 60 % of EPS = 60 % of Rs.5 =
Rs. 3
iii.
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital including Retained Earnings |
7,00,000 |
7,00,000/
10,00,000 = 0.7 |
0.21 |
0.147 |
|
12
% Debentures |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000/
10,00,000 =.3 |
.072 |
0.0216 |
|
Total |
10,00,000 |
WACC = ∑ Weighted
Cost = 0.147+ 0.0216 = 0.1686 = 16.86 % |
||
25. ABC company has the following capital structure and is considered to be an optimum.
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Share Capital- 1,00,000 shares |
16,00,000 |
|
15 % Preference Shares |
1,00,000 |
|
20 % Debentures |
3,00,000 |
|
|
20,00,000 |
The company has paid a dividend of Rs. 4
with a growth rate of 10%. The company's share has a current market price of
Rs. 20 per share. The expected dividend per share next year is 50% of the
dividend for the current year. 20 % new debentures can be issued by the
company. The company's debentures are currently selling at Rs. 98 per
debenture. 15 % preference share can be sold at a net price of Rs. 9.5 (face
value Rs. 10 each). The company's tax rate is 30%.
(a) Calculate after tax cost of (i) Debt,
(ii) Preference share capital and (iii) Equity shares
(b) Also calculate Weighted Average Cost
of Capital, WACC.
Solution
After tax cost of new Debt (Kd) =
= 1.5 / 9.5 = 0.158 = 15.8%
Cost
of Equity (Ke) = (D1 / MP) + g
D1 = 50 % of D0 = 50 % of Rs.4
= Rs. 2
|
|
Book
Value (Rs) |
Weight
|
After
Tax Cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Share
Capital |
16,00,000 |
16,00,000/
20,00,000 = 0.8 |
0.20 |
0.16 |
|
15
% Preference Shares |
1,00,000 |
1,00,000/
20,00,000 =.05 |
.158 |
0.008 |
|
20
% Debentures |
3,00,000 |
3,00,000/
20,00,000 =.15 |
.1429 |
.0214 |
|
|
20,00,000 |
WACC based on Book Value = ∑ Weighted
Cost = 0.16 + 0.008 + .0214 = .1894 = 18.94 % |
||
26. RBL & Co. wishes to find out its
weighted marginal cost of capital, WMCC, based on target capital structure
proportions. Using the data given below, find out the WMCC.
|
Source |
Proportion |
Range |
Cost |
|
Equity share capital
|
50% |
Up to Rs. 3,00,000 3,00,000-7,50,000 7,50,000 and above |
13.00% 13.5% 15.5% |
|
Preference shares |
10% |
Up to 1,00,000 1,00,000 and above |
10 % 11% |
|
Long term debt
|
40% |
Up to Rs. 4,00,000 4,00,000-8,00,000 8,00,000 and above |
6 % 6.50% 7 % |
Solution
|
Source |
Prop. |
Range |
Cost |
Breaking
Points |
|
E.
Share |
.5 |
Up
to Rs. 3,00,000 3,00,000-7,50,000 7,50,000
and above |
13.00% 13.5% 15.5% |
3
L /.5=6 L 7.5
L /.5=15L-------------- |
|
P.
Share |
.1 |
Up
to 1,00,000 1,00,000
and above |
10
% 11% |
1
L / .1 = 10 L -------------- |
|
L.T.
Debt
|
.4 |
Up
to Rs. 4,00,000 4,00,000-8,00,000 8,00,000
and above |
6
% 6.50% 7
% |
4
L / .4 = 10L 8
L / .4 = 20 L --------------- |
|
Range |
Source |
Prop. |
cost |
Weighted
Cost = Weight × After Tax Cost |
|
Up
to 6 L |
E.
Share P.
Share L
T Debt
|
.5 .1 .4 |
.13 .1 .06 |
.065 .01 .024 WMCC=.099
|
|
6
L – 10 L |
E.
Share P.
Share L
T Debt |
.5 .1 .4 |
.135 .1 .06 |
.0675 .01 .024 WMCC=.1015 |
|
10
L – 15 L |
E.
Share P.
Share L
T Debt |
.5 .1 .4 |
.135 .11 .065 |
.0675 .011 .026 WMCC=.1045 |
|
15
L – 20 L |
E.
Share P.
Share L
T Debt |
.5 .1 .4 |
.155 .11 .065 |
.0775 .011 .026 WMCC=.1145 |
|
20
L & above |
E.
Share P.
Share L
T Debt |
.5 .1 .4 |
.155 .11 .07 |
.0775 .011 .028 WMCC=.1165 |
Links to Financial Management notes: -
Time Value of Money
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-formulae-financial.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-i-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-2-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/time-value-of-money-part-3-solved.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/time-value-of-money-i-financial.html
Leverage Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/financial-management-notes-leverage.html
Cost of Capital
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/cost-of-capital-solved-problems.html
EBIT – EPS Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/08/ebit-eps-analysis-financial-break-even.html
Capital Structure Analysis
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/02/capital-structure-theories-solved.html
Planning & Designing of Capital Structure
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/03/planning-designing-of-capital-structure.html
Estimation of Cash Flow in Capital Budgeting
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-1-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-2-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/part-3-estimation-of-cash-flow-in.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2022/03/estimation-of-cash-flow-in-capital.html
Techniques of Capital Budgeting
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/techniques-of-capital-budgeting.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/capital-budgeting-i-httprblacademycom.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/05/financial-management-capital-budgeting.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved_2.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved_14.html
https://rblacademy.blogspot.com/2021/06/techniques-of-capital-budgeting-solved.html